Translating entities in EasyAdmin with DoctrineBehaviors
Table of Contents
In this article we will look at how to translate entities in EasyAdmin. We will create an "Article" entity, where we can translate title, slug and content into several languages, as well as add the ability to filter by translatable fields.
Database design approaches for multi-language websites
One of the challenges we face when developing multi-lingual applications is storing translatable entity properties. There are several database design approaches for this task, but the 2 most common ones are:
-
Single Translation Table Approach
All translations are stored in a single table, the structure of which may look something like the following:
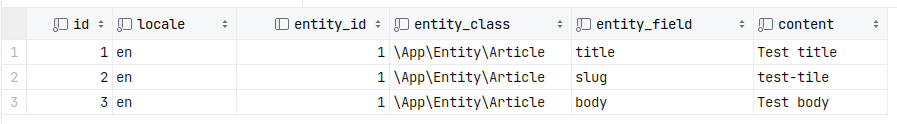
-
Additional Translation Table Approach
A separate table containing only translations of that entity is created for each entity to be translated. Each row in such a table is a translation of all properties of the entity into a specific language. An example of the structure of such a table: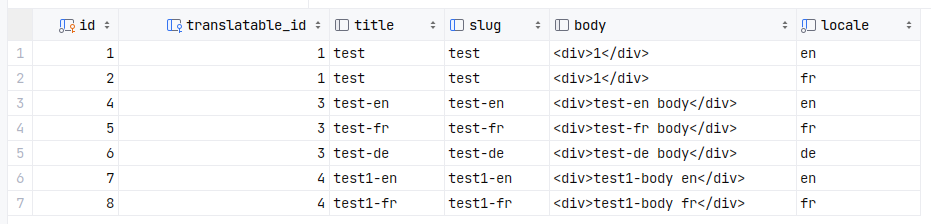
In this article, we will look at the second approach - Additional Translation Table.
Project setup
First, let's install EasyAdmin, as well as knplabs/doctrine-behaviors and a2lix/translation-form-bundle packages, which will allow us to simplify the implementation of multilingualism.
composer require easycorp/easyadmin-bundle knplabs/doctrine-behaviors a2lix/translation-form-bundle
We will add 3 languages: 2 of them will be mandatory when editing an entity (English and French), and 1 additional language (German). The default language will be English.
Create a config/packages/a2lix.yaml file with the following contents:
a2lix_translation_form:
locale_provider: default
locales: [en, fr, de]
default_locale: en
required_locales: [en, fr]
templating: "@A2lixTranslationForm/bootstrap_5_layout.html.twig"
Create an entity Article with Symfony Maker. This entity should contain only non-translatable properties and must implement the TranslationInterface interface and use the Translatable trait:
<?php
namespace App\Entity;
use App\Repository\ArticleRepository;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
use Knp\DoctrineBehaviors\Contract\Entity\TranslatableInterface;
use Knp\DoctrineBehaviors\Model\Translatable\TranslatableTrait;
use Symfony\Component\PropertyAccess\PropertyAccess;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: ArticleRepository::class)]
class Article implements TranslatableInterface
{
use TranslatableTrait;
#[ORM\Id]
#[ORM\GeneratedValue]
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $id = null;
public function getId(): ?int
{
return $this->id;
}
}
And let's also add the magic __get method, thanks to which we can get translated properties (e.g., $article->getTitle()):
<?php
use Symfony\Component\PropertyAccess\PropertyAccess;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: ArticleRepository::class)]
class Article implements TranslatableInterface
{
...
public function __get($name)
{
return PropertyAccess::createPropertyAccessor()->getValue($this->translate(), $name);
}
}
Create a second entity that will contain the properties to be translated. In our example, these are title, slug and body. According to the naming convention, the name of this entity must be Article). Accordingly, the new entity is ArticleTranslation.
This entity must implement the TranslationInterface interface and use the TranslationTrait trait.
<?php
namespace App\Entity;
use App\Repository\ArticleTranslationRepository;
use Doctrine\DBAL\Types\Types;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping\UniqueConstraint;
use Knp\DoctrineBehaviors\Contract\Entity\TranslationInterface;
use Knp\DoctrineBehaviors\Model\Translatable\TranslationTrait;
use Symfony\Bridge\Doctrine\Validator\Constraints\UniqueEntity;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints\Length;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: ArticleTranslationRepository::class)]
#[UniqueConstraint(name: "locale_slug_uidx", columns: ['locale', 'slug'])]
#[UniqueEntity(['locale', 'slug'])]
class ArticleTranslation implements TranslationInterface
{
use TranslationTrait;
#[ORM\Id]
#[ORM\GeneratedValue]
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $id = null;
#[ORM\Column(length: 255, nullable: true)]
#[Length(min: 3)]
private ?string $title = null;
#[ORM\Column(length: 255, nullable: true)]
private ?string $slug = null;
#[ORM\Column(type: Types::TEXT, nullable: true)]
private ?string $body = null;
// GETTERS AND SETTERS
}
All fields are nullable, so empty translations can be saved for additional languages. I also added a unique index on locale and slug.
Now we need to create a migration for the new entities and run it:
bin/console make:migration
bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate
Translating entities in EasyAdmin
Let's move on to creating the administrative backend using EasyAdmin. Create a new Dashboard and CRUD for the Article entity:
bin/console make:admin:dashboard
bin/console make:admin:crud
Add a link to Article crud in configureMenuItems() in the DashboardController:
<?php
class DashboardController extends AbstractDashboardController
{
...
public function configureMenuItems(): iterable
{
yield MenuItem::linkToCrud('Articles', 'fas fa-pen', Article::class);
}
}
We proceed to the implementation of the entity translation functionality in EasyAdmin.
Option 1
A quick solution is to create a new TranslationsSimpleField custom field in EasyAdmin, into which to pass an array with parameters for TranslationsType form type from the a2lix/translation-form-bundle package:
<?php
namespace App\EasyAdmin\Field;
use A2lix\TranslationFormBundle\Form\Type\TranslationsType;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Contracts\Field\FieldInterface;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\FieldTrait;
class TranslationsSimpleField implements FieldInterface
{
use FieldTrait;
public static function new(string $propertyName, ?string $label = null, $fieldsConfig = []): self
{
return (new self())
->setProperty($propertyName)
->setLabel($label)
->onlyOnForms()
->setRequired(true)
->setFormType(TranslationsType::class)
->setFormTypeOptions([
'fields' => $fieldsConfig,
])
;
}
}
An then return/yield that field from the configureFields() method of ArticleCrudController:
<?php
class ArticleCrudController extends AbstractCrudController
{
...
public function configureFields(string $pageName): iterable
{
yield TranslationsSimpleField::new('translations', null, [
'title' => [
'field_type' => TextType::class,
'required' => true,
],
'slug' => [
'field_type' => SlugType::class,
'required' => true,
],
'body' => [
'field_type' => TextEditorType::class,
'required' => true,
],
]);
}
}
But in this case, you will need to reverse engineer the EasyAdmin fields you want to use and their configurators, then manually pass options to each form type and load the resources and themes.
Option 2
Here's an idea. How about creating a new custom EasyAdmin TranslationsField field, and passing to it other EasyAdmin fields (that we need to translate) through addTranslatableField() method? With this implementation, we will be able to add translatable fields much easier:
<?php
class ArticleCrudController extends AbstractCrudController
{
...
public function configureFields(string $pageName): iterable
{
yield TranslationsField::new('translations')
->addTranslatableField(TextField::new('title'))
->addTranslatableField(SlugField::new('slug'))
->addTranslatableField(TextEditorField::new('body'))
;
}
}
I like the second approach better because it's cleaner and much easier to use later. And here's how we can do it.
Creating a custom TranslationsField field
Create a new class App\EasyAdmin\Field\TranslationsField. It must implement the FieldInterface interface and use the FieldTrait trait. And add the addTranslatableField() method:
<?php
namespace App\EasyAdmin\Field;
use A2lix\TranslationFormBundle\Form\Type\TranslationsType;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Contracts\Field\FieldInterface;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\FieldTrait;
class TranslationsField implements FieldInterface
{
use FieldTrait;
public const OPTION_FIELDS_CONFIG = 'fieldsConfig';
public static function new(string $propertyName, ?string $label = null): self
{
return (new self())
->setProperty($propertyName)
->setLabel($label)
->onlyOnForms()
->setRequired(true)
->addFormTheme('admin/crud/form/field/translations.html.twig')
->addCssFiles('build/translations-field.css')
->setFormType(TranslationsType::class)
->setFormTypeOption('block_prefix', 'translations_field')
;
}
public function addTranslatableField(FieldInterface $field): self
{
$fieldsConfig = (array)$this->getAsDto()->getCustomOption(self::OPTION_FIELDS_CONFIG);
$fieldsConfig[] = $field;
$this->setCustomOption(self::OPTION_FIELDS_CONFIG, $fieldsConfig);
return $this;
}
}
Create a form theme admin/crud/form/field/translations.html.twig with the following content:
{% block a2lix_translations_widget %}
{{ form_errors(form) }}
<div class="a2lix_translations form-tabs">
<ul class="a2lix_translationsLocales nav nav-tabs" role="tablist">
{% for translationsFields in form %}
{% set locale = translationsFields.vars.name %}
{% set errorsNumber = 0 %}
{% for translation in form | filter(translation => translation.vars.name == locale) %}
{% for translationField in translation.children %}
{% if translationField.vars.errors|length %}
{% set errorsNumber = errorsNumber + translationField.vars.errors|length %}
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
{% endfor %}
<li class="nav-item">
<a href="#{{ translationsFields.vars.id }}_a2lix_translations-fields" class="nav-link {% if app.request.locale == locale %}active{% endif %}" data-bs-toggle="tab" role="tab">
{{ translationsFields.vars.label|default(locale|humanize)|trans }}
{% if translationsFields.vars.required %}<span class="locale-required"></span>{% endif %}
{% if errorsNumber > 0 %}<span class="badge badge-danger" title="{{ errorsNumber }}">{{ errorsNumber }}</span>{% endif %}
</a>
</li>
{% endfor %}
</ul>
<div class="a2lix_translationsFields tab-content">
{% for translationsFields in form %}
{% set locale = translationsFields.vars.name %}
<div id="{{ translationsFields.vars.id }}_a2lix_translations-fields" class="tab-pane {% if app.request.locale == locale %}show active{% endif %} {% if not form.vars.valid %}sonata-ba-field-error{% endif %}" role="tabpanel">
{{ form_errors(translationsFields) }}
{{ form_widget(translationsFields, {'attr': {'class': 'row'}} ) }}
</div>
{% endfor %}
</div>
</div>
{% endblock %}
{% block a2lix_translations_label %}{% endblock %}
{% block a2lix_translationsForms_widget %}
{{ block('a2lix_translations_widget') }}
{% endblock %}
I used the template @A2lixTranslationForm/bootstrap_5_layout.html.twig as a base, but modified it for EasyAdmin (tabs, required fields, number of errors).
Also, add a styles file build/translations-field.css with the following content:
.a2lix_translations > .nav-tabs .nav-item .locale-required:after {
background: var(--color-danger);
border-radius: 50%;
content: "";
display: inline-block;
filter: opacity(75%);
height: 4px;
position: relative;
right: -2px;
top: -8px;
width: 4px;
z-index: var(--zindex-700);
}
Most likely you will use webpack in your work project, but to simplify the tutorial, I'll use css files.
Creating a Configurator for the TranslationsField
We also need a Configurator for the TranslationsField. Create a new class App\EasyAdmin\Field\Configurator\TranslationsConfigurator, which will implement the FieldConfiguratorInterface. The TranslationsField configurator must pass to TranslationsType required form types for each property to be translated with options for these form types.
<?php
namespace App\EasyAdmin\Field\Configurator;
use App\EasyAdmin\Field\TranslationsField;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Collection\FieldCollection;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Context\AdminContext;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Contracts\Field\FieldConfiguratorInterface;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Dto\EntityDto;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Dto\FieldDto;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints\Valid;
class TranslationsConfigurator implements FieldConfiguratorInterface
{
public function __construct(private iterable $fieldConfigurators)
{
}
public function supports(FieldDto $field, EntityDto $entityDto): bool
{
return $field->getFieldFqcn() === TranslationsField::class;
}
public function configure(FieldDto $field, EntityDto $entityDto, AdminContext $context): void
{
$formTypeOptionsFields = [];
$fieldsCollection = FieldCollection::new(
(array) $field->getCustomOption(TranslationsField::OPTION_FIELDS_CONFIG)
);
foreach ($fieldsCollection as $dto) {
/** @var FieldDto $dto */
// run field configurator manually as translatable fields are not returned/yielded from configureFields()
foreach ($this->fieldConfigurators as $configurator) {
if (!$configurator->supports($dto, $entityDto)) {
continue;
}
$configurator->configure($dto, $entityDto, $context);
}
foreach ($dto->getFormThemes() as $formThemePath) {
$context?->getCrud()?->addFormTheme($formThemePath);
}
// add translatable fields assets
$context->getAssets()->mergeWith($dto->getAssets());
$dto->setFormTypeOption('field_type', $dto->getFormType());
$formTypeOptionsFields[$dto->getProperty()] = $dto->getFormTypeOptions();
}
$field->setFormTypeOptions([
'ea_fields' => $fieldsCollection,
'fields' => $formTypeOptionsFields,
'constraints' => [
new Valid(),
],
]);
}
}
Since we will not return these fields in the configureFields() method of ArticleCrudController, EasyAdmin will not know anything about them by default. So we will manually run the configurators for the added fields, and load their assets (css and js).
Add this field configurator to config/services.yml:
App\EasyAdmin\Field\Configurator\TranslationsConfigurator:
arguments:
$fieldConfigurators: !tagged_iterator ea.field_configurator
tags:
- { name: 'ea.field_configurator', priority: -10 }
Creating a Form Type Extension
One more thing. EasyAdmin passes some properties required for display through the FormView variable ea_crud_form. Since EasyAdmin knows nothing about our fields, we will pass ea_crud_form value manually as well.
Create a new extension for the TranslationsType form type in the App\Form\Extension\TranslationsTypeExtension class with the following content:
<?php
namespace App\Form\Extension;
use A2lix\TranslationFormBundle\Form\Type\TranslationsType;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Collection\FieldCollection;
use Symfony\Component\Form\AbstractTypeExtension;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormInterface;
use Symfony\Component\Form\FormView;
use Symfony\Component\OptionsResolver\OptionsResolver;
class TranslationsTypeExtension extends AbstractTypeExtension
{
public static function getExtendedTypes(): iterable
{
return [TranslationsType::class];
}
public function configureOptions(OptionsResolver $resolver)
{
$resolver->setRequired('ea_fields');
$resolver->setAllowedTypes('ea_fields', FieldCollection::class);
}
public function finishView(FormView $view, FormInterface $form, array $options)
{
/** @var FieldCollection $fields */
$fields = $options['ea_fields'];
foreach ($view->children as $translationView) {
foreach ($translationView->children as $fieldView) {
$fieldView->vars['ea_crud_form'] = [
'ea_field' => $fields->getByProperty($fieldView->vars['name'])
];
}
}
}
}
That's all we need. All that remains is to add the TranslationsField to the configureFields() method of the ArticleCrudController:
<?php
namespace App\Controller\Admin;
use App\EasyAdmin\Field\TranslationsField;
use App\EasyAdmin\Filter\TranslatableTextFilter;
use App\Entity\Article;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Config\Filters;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Controller\AbstractCrudController;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\IdField;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\SlugField;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\TextEditorField;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Field\TextField;
class ArticleCrudController extends AbstractCrudController
{
...
public function configureFields(string $pageName): iterable
{
yield IdField::new('id')->hideOnForm();
yield TranslationsField::new('translations')
->addTranslatableField(
TextField::new('title')->setRequired(true)->setHelp('Help message for title')->setColumns(12)
)
->addTranslatableField(
SlugField::new('slug')->setTargetFieldName('title')->setRequired(true)->setHelp('Help message for slug')->setColumns(12)
)
->addTranslatableField(
TextEditorField::new('body')->setRequired(true)->setHelp('Help message for body')->setNumOfRows(6)->setColumns(12)
)
;
}
}
Now go to the "Create Article" page in the administrative backend, and you will see the title, slug, body translation fields:
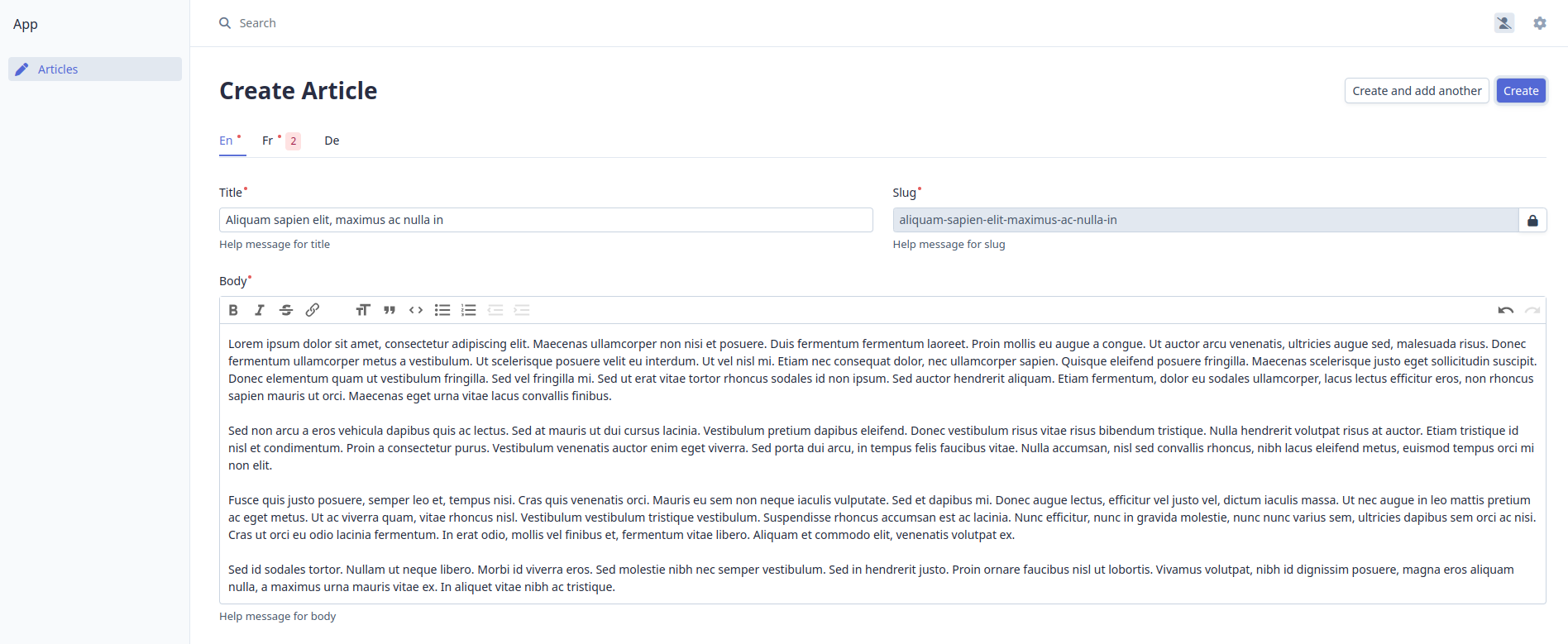
Thanks to our TranslationsConfigurator field configurator and TranslationsTypeExtension form extension, all field parameters (e.g., help, columns, etc.) are passed automatically to TranslationsType.
Creating a filter for translatable fields
To be able to filter articles by translatable fields, create a new custom filter \App\EasyAdmin\Filter\TranslatableTextFilter with the following contents:
<?php
namespace App\EasyAdmin\Filter;
use Doctrine\ORM\QueryBuilder;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Contracts\Filter\FilterInterface;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Dto\EntityDto;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Dto\FieldDto;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Dto\FilterDataDto;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Filter\FilterTrait;
use EasyCorp\Bundle\EasyAdminBundle\Form\Filter\Type\TextFilterType;
class TranslatableTextFilter implements FilterInterface
{
use FilterTrait;
public static function new(string $propertyName, $label = null): self
{
return (new self())
->setFilterFqcn(__CLASS__)
->setProperty($propertyName)
->setLabel($label)
->setFormType(TextFilterType::class)
->setFormTypeOption('translation_domain', 'messages')
;
}
public function apply(QueryBuilder $queryBuilder, FilterDataDto $filterDataDto, ?FieldDto $fieldDto, EntityDto $entityDto): void
{
$alias = $filterDataDto->getEntityAlias();
$property = $filterDataDto->getProperty();
$comparison = $filterDataDto->getComparison();
$parameterName = $filterDataDto->getParameterName();
$value = $filterDataDto->getValue();
$queryBuilder
->leftJoin(sprintf('%s.translations', $alias), sprintf('%s_t', $alias))
->andWhere(sprintf('%s_t.%s %s :%s', $alias, $property, $comparison, $parameterName))
->setParameter($parameterName, $value)
;
}
}
And then you can use it like any other filter in EasyAdmin:
<?php
class ArticleCrudController extends AbstractCrudController
{
...
public function configureFilters(Filters $filters): Filters
{
return $filters
->add(TranslatableTextFilter::new('title'))
;
}
...
}

You can see the full code on github https://github.com/dzhebrak/easyadmin-translation-form-demo/